Determining the minimally clinically important difference for the Pediatric Liver Transplant Quality of Life (PeLTQL) questionnaire, a pilot cohort study
Simone Kortbeek1, Fatema T Johara2,3, Tomisin John2,3, Vicky L Ng2,3.
1Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Alberta Children's Hospital, Cumming School of Medicine, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada; 2Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, The Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada; 3Transplant and Regenerative Medicine Centre, The Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Introduction: Completion of the Pediatric Liver Transplant Quality of Life (PeLTQL) questionnaire, a patient-reported outcome measure for pediatric liver transplant (LT) recipients, generates a total and three subdomain scores (Social Emotional, Coping & Adjustment and Future Health). Published methodologies exist to derive the minimally clinically important difference (MCID), referring to the change in score that reflects a meaningful change for the patient. We used two established approaches to derive the MCID values for the PeLTQL.
Method: All self- and proxy- reported PeLTQL surveys completed during routine surveillance visits at SickKids LT clinic were reviewed. Surveys with data from two sequential visits were included in analysis. Anchor and distribution-based (0.5 standard deviation, standard error of measurement) methods were used to ascertain MCID values for PeLTQL. Given the retrospective study design, an internal anchor question was used.
Results: PeLTQL data from 65 LT recipients (26 [40%] male, 17 [42%] biliary atresia, median age at LT 3.08 years [IQR 0.99 - 7.30]), and their caregivers were included for analysis. Median patient age at time of baseline PeLTQL completion was 9.05 (IQR 5.70 - 11.43) years. The MCID for self-PeLTQL total scores ranged from 4.53 to 8.10 and from 4.49 to 8.75 for caregiver responses (Table 1).
Conclusion: The results of this study may guide clinicians in the interpretation of PeLTQL results with attention to respondents with a change in score of >4.5 points. Prospective multi-center studies utilizing an external anchor question will add to knowledge about MCID values for the PeLTQL. 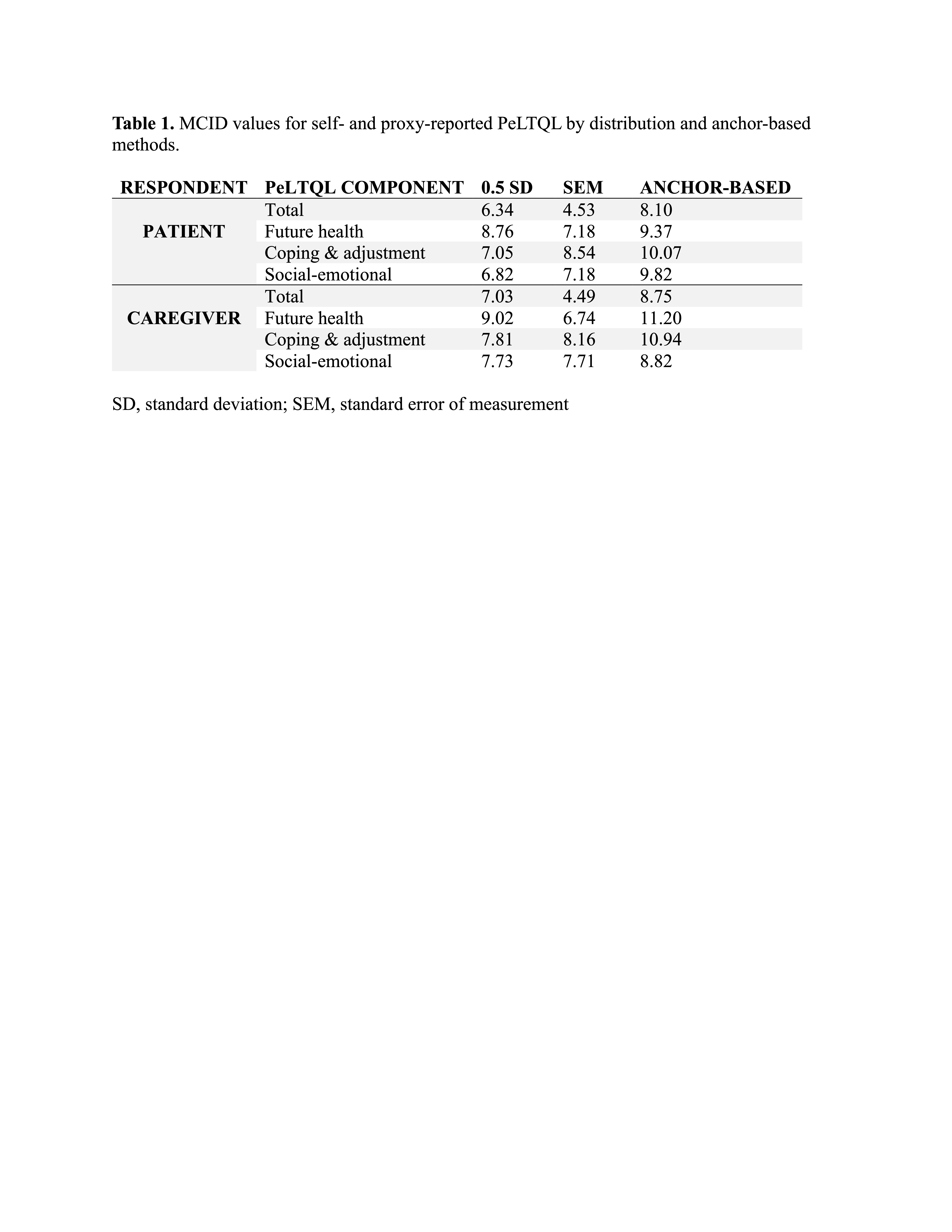
If you have any questions during the meeting, please go to the registration desk. Our emails will be monitored sporadically.
REGISTRATION DESK OPENING TIMES
Sunday, October 15, 16:00-18:00 Monday, October 16, 07:00-18:00 Tuesday October 17, 07:00-12:30